SpinalHDL 内部数据模型
简介
本页面提供有关 SpinalHDL 使用的内部数据结构的文档,用于存储和修改用户通过 SpinalHDL API 描述的网表。
总体结构
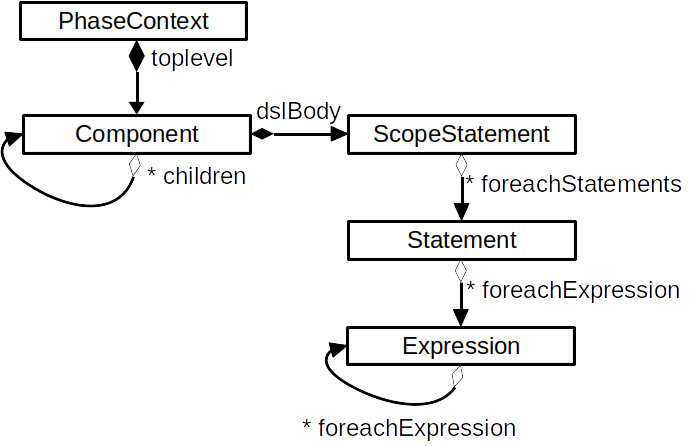
下图遵循 UML 命名法:
带有白色箭头的链接表示“源继承目标”
带有黑色菱形的链接表示“源包含目标”
带有白色菱形的链接意味着“源中有一个对目标的引用”
``* `` 符号表示“多个”
大多数数据结构都是使用双向链表存储,这方便了元素的插入和删除。
全局数据结构图如下:
这里是关于 Statement 类的更多细节:
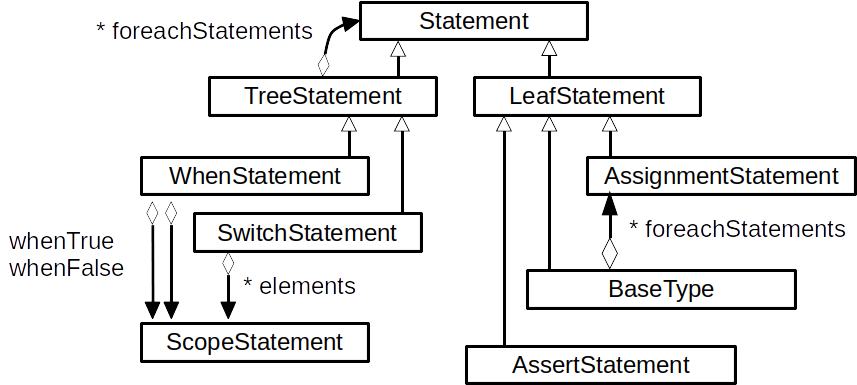
一般来说,当数据模型内的元素使用其他表达式或语句时,该元素通常包括迭代这些用法的函数。例如,每个表达式都配有一个 foreachExpression 函数。
使用这些迭代函数时,您也可以从树中删除当前元素。
此外,作为旁注,虽然 foreachXXX 函数仅迭代一层深度,但通常有相应的 walkXXX 函数执行递归迭代。例如,在 ((a+b)+c)+d 表达式上使用 myExpression.walkExpression ,这将遍历整个加法运算树。
还有像 myExpression.remapExpressions(Expression => Expression), 这样的实用工具,它会迭代 myExpression 中使用的所有表达式,并将它们替换为您提供的表达式。
More generally, most of the graph checks and transformations done by SpinalHDL are located in <https://github.com/SpinalHDL/SpinalHDL/blob/dev/core/src/main/scala/spinal/core/internals/Phase.scala>
探索数据模型
在不使用快捷方式的情况下,识别网表中所有加法器的示例如下 :
object FindAllAddersManually {
class Toplevel extends Component {
val a,b,c = in UInt(8 bits)
val result = out(a + b + c)
}
import spinal.core.internals._
class PrintBaseTypes(message : String) extends Phase {
override def impl(pc: PhaseContext) = {
println(message)
recComponent(pc.topLevel)
def recComponent(c: Component): Unit = {
c.children.foreach(recComponent)
c.dslBody.foreachStatements(recStatement)
}
def recStatement(s: Statement): Unit = {
s.foreachExpression(recExpression)
s match {
case ts: TreeStatement => ts.foreachStatements(recStatement)
case _ =>
}
}
def recExpression(e: Expression): Unit = {
e match {
case op: Operator.BitVector.Add => println(s"Found ${op.left} + ${op.right}")
case _ =>
}
e.foreachExpression(recExpression)
}
}
override def hasNetlistImpact = false
override def toString = s"${super.toString} - $message"
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val config = SpinalConfig()
// Add a early phase
config.addTransformationPhase(new PrintBaseTypes("Early"))
// Add a late phase
config.phasesInserters += {phases =>
phases.insert(phases.indexWhere(_.isInstanceOf[PhaseVerilog]), new PrintBaseTypes("Late"))
}
config.generateVerilog(new Toplevel())
}
}
这将生成:
[Runtime] SpinalHDL v1.6.1 git head : 3100c81b37a04715d05d9b9873c3df07a0786a9b
[Runtime] JVM max memory : 8044.0MiB
[Runtime] Current date : 2021.10.16 20:31:33
[Progress] at 0.000 : Elaborate components
[Progress] at 0.163 : Checks and transforms
Early
Found (toplevel/a : in UInt[8 bits]) + (toplevel/b : in UInt[8 bits])
Found (toplevel/??? : UInt[? bits]) + (toplevel/c : in UInt[8 bits])
[Progress] at 0.191 : Generate Verilog
Late
Found (UInt + UInt)[8 bits] + (toplevel/c : in UInt[8 bits])
Found (toplevel/a : in UInt[8 bits]) + (toplevel/b : in UInt[8 bits])
[Done] at 0.218
请注意,在许多情况下,都可以使用快捷方式。前面提到的所有递归过程,都可以用一个递归过程代替。 :
override def impl(pc: PhaseContext) = {
println(message)
pc.walkExpression {
case op: Operator.BitVector.Add => println(s"Found ${op.left} + ${op.right}")
case _ =>
}
}
编译环节
以下是按顺序排列的默认环节的完整列表,用于从顶级组件修改、检查和生成 Verilog 代码。 :
如果您作为用户使用 SpinalConfig.addTransformationPhase(new MyPhase()) 添加新的编译环节,则该环节将在用户组件实例细化后立即插入,这在编译序列中相对较早。在此环节,您仍然可以使用完整的 SpinalHDL 用户 API 将元素引入网表。
如果您选择使用 SpinalConfig.phasesInserters API,则必须谨慎行事并确保对网表所做的任何修改与已执行的阶段保持一致。例如,如果您在 PhaseInferWidth 之后插入环节,则必须指定引入的每个节点的位宽。
在不使用插件的情况下,以用户身份修改网表
有多个用户 API 使您能够在用户实例细化环节进行修改。 :
mySignal.removeAssignments :将删除所有先前对给定信号的赋值 :=
mySignal.removeStatement : Will void the existence of the signal
mySignal.setAsDirectionLess :将输入/输出信号转换为内部信号(无方向)
mySignal.setName :在信号上强制指定名称(还有许多其他变体)
mySubComponent.mySignal.pull() :将提供给定信号的可读副本,即使该信号位于层次结构中的其他位置
myComponent.rework{ myCode } :在 myComponent 上下文中执行 myCode,允许使用用户 API 修改它
例如,以下代码可用于修改顶级组件,向组件的每个输入和输出添加三级移位寄存器。这对于综合器测试特别有用。
def ffIo[T <: Component](c : T): T = {
def buf1[T <: Data](that : T) = KeepAttribute(RegNext(that)).addAttribute("DONT_TOUCH")
def buf[T <: Data](that : T) = buf1(buf1(buf1(that)))
c.rework {
val ios = c.getAllIo.toList
ios.foreach{io =>
if(io.getName() == "clk") {
// Do nothing
} else if(io.isInput) {
io.setAsDirectionLess().allowDirectionLessIo // allowDirectionLessIo is to disable the io Bundle linting
io := buf(in(cloneOf(io).setName(io.getName() + "_wrap")))
} else if(io.isOutput) {
io.setAsDirectionLess().allowDirectionLessIo
out(cloneOf(io).setName(io.getName() + "_wrap")) := buf(io)
} else ???
}
}
c
}
您可以通过以下方式使用该代码:
SpinalVerilog(ffIo(new MyToplevel))
这是一个函数,使您能够执行主体代码,就好像当前组件的上下文不存在一样。这对于定义新信号特别有用,这样信号不受当前条件范围(例如when或switch)的影响。
def atBeginingOfCurrentComponent[T](body : => T) : T = {
val body = Component.current.dslBody // Get the head of the current component symbols tree (AST in other words)
val ctx = body.push() // Now all access to the SpinalHDL API will be append to it (instead of the current context)
val swapContext = body.swap() // Empty the symbol tree (but keep a reference to the old content)
val ret = that // Execute the block of code (will be added to the recently empty body)
ctx.restore() // Restore the original context in which this function was called
swapContext.appendBack() // append the original symbols tree to the modified body
ret // return the value returned by that
}
val database = mutable.HashMap[Any, Bool]()
def get(key : Any) : Bool = {
database.getOrElseUpdate(key, atBeginingOfCurrentComponent(False)
}
object key
when(something) {
if(somehow) {
get(key) := True
}
}
when(database(key)) {
...
}
例如,这种功能被用在 VexRiscv 管道中,以根据需要动态创建组件或元素。
用户空间网表分析
SpinalHDL 的数据模型也是可访问的,并且可以在用户实力细化时读取。下面的示例可以帮助找到遍历信号列表的最短逻辑路径(就时钟周期而言)。在本例中,它用于分析 VexRiscv FPU 设计的延迟。
println("cpuDecode to fpuDispatch " + LatencyAnalysis(vex.decode.arbitration.isValid, logic.decode.input.valid))
println("fpuDispatch to cpuRsp " + LatencyAnalysis(logic.decode.input.valid, plugin.port.rsp.valid))
println("cpuWriteback to fpuAdd " + LatencyAnalysis(vex.writeBack.input(plugin.FPU_COMMIT), logic.commitLogic(0).add.counter))
println("add " + LatencyAnalysis(logic.decode.add.rs1.mantissa, logic.get.merge.arbitrated.value.mantissa))
println("mul " + LatencyAnalysis(logic.decode.mul.rs1.mantissa, logic.get.merge.arbitrated.value.mantissa))
println("fma " + LatencyAnalysis(logic.decode.mul.rs1.mantissa, logic.get.decode.add.rs1.mantissa, logic.get.merge.arbitrated.value.mantissa))
println("short " + LatencyAnalysis(logic.decode.shortPip.rs1.mantissa, logic.get.merge.arbitrated.value.mantissa))
在这里您可以找到该 LatencyAnalysis 工具的实现:<https://github.com/SpinalHDL/SpinalHDL/blob/3b87c898cb94dc08456b4fe2b1e8b145e6c86f63/lib/src/main/scala/spinal/lib/Utils.scala#L620>
遍历、枚举正在使用的每个时钟域
在本例中,这是在实例细化完成之后利用 SpinalHDL 报告完成的。
object MyTopLevelVerilog extends App {
class MyTopLevel extends Component {
val cdA = ClockDomain.external("rawrr")
val regA = cdA(RegNext(False))
val sub = new Component {
val cdB = ClockDomain.external("miaou")
val regB = cdB(RegNext(False))
val clkC = CombInit(regB)
val cdC = ClockDomain(clkC)
val regC = cdC(RegNext(False))
}
}
val report = SpinalVerilog(new MyTopLevel)
val clockDomains = mutable.LinkedHashSet[ClockDomain]()
report.toplevel.walkComponents(c =>
c.dslBody.walkStatements(s =>
s.foreachClockDomain(cd =>
clockDomains += cd
)
)
)
println("ClockDomains : " + clockDomains.mkString(", "))
val externals = clockDomains.filter(_.clock.component == null)
println("Externals : " + externals.mkString(", "))
}
打印信息是
ClockDomains : rawrr_clk, miaou_clk, clkC
Externals : rawrr_clk, miaou_clk